Ray Tracers
The calculation of seismic travel times is a cornerstone for the migration and stacking approach. Qseek supports different ray tracers for travel time calculation, which can be adapted for different geological settings.
Constant Velocity
The constant velocity models is trivial and follows:
This module is used for simple use cases and cross-referencing testing.
ConstantVelocityTracer Module
Travel time tracer with a constant velocity.
1D Layered Velocity Model
Travel times for 1D layered velocity models can be calculated by two different modules.
FastMarchingTracer Module
Travel time calculation for layered 1D velocity models.
Calculation is based on fast marching method to solve the Eikonal solution. This the more perfomant than the Pyrocko Cake ray tracer, especially for large number of stations and nodes.
velocity_model-
Velocity model for the ray tracer.
interpolation_method:nearest | linear | cubic-
Interpolation method for travel times in the volume. Choose from
nearest,linearorcubic. nthreads:0-
Number of threads to use for travel time. If set to
0,cpu_count*2will be used. implementation:pyrocko | scikit-fmm-
Implementation of the Fast Marching Method. Pyrocko only supports first-order FMM for now.
phases-
Phases to calculate.
{
"tracer": "FastMarching",
"velocity_model": {
"filename": "/home/marius/.cache/qseek/velocity_models/default.nd",
"format": "nd",
"crust2_profile": "",
"raw_file_data": null
},
"interpolation_method": "linear",
"nthreads": 0,
"implementation": "pyrocko",
"phases": [
"fm:P",
"fm:S"
]
}
Calculation of travel times in 1D layered media is based on the Pyrocko Cake ray tracer.
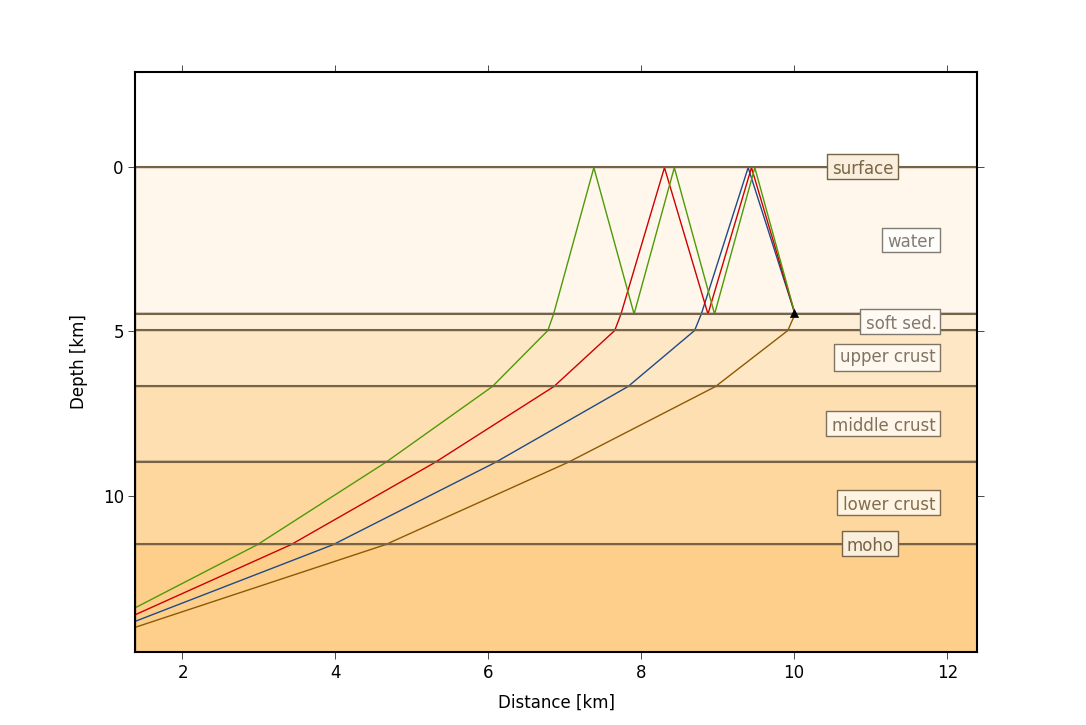
Pyrocko Cake 1D ray tracer for travel time calculation in 1D layered media
CakeTracer Module
Travel time calculation for 1D layered velocity models.
Calculation is based on Pyrocko Cake ray tracer.
phases-
Dictionary of phases and timings to calculate.
earthmodel-
Earth model to calculate travel times for.
3D Velocity Model 🚀
We implement the fast marching method for calculating first arrivals of waves in 3D volumes. Currently three different 3D velocity models are supported:
- Import NonLinLoc 3D velocity model
- 1D layered model 🥞
- Constant velocity, mainly for testing purposes 🥼

Conceptual 2D visualisation for seismic traveltimes calculation in heterogenous media using the fast-marching method for the Eikonal solution is presented. Traveltimes from the receiving station at the surface (indicated by a yellow triangle) towards the subsurface grid are calculated, resulting in station-specifig traveltimes for all potential source locations simultaneously.
FastMarching3DTracer Module
Travel time ray tracer using the Fast Marching Method for 3D earth models.
interpolation_method:nearest | linear | cubic-
Interpolation method for travel times in the volume. Choose from
nearest,linearorcubic. nthreads:0-
Number of threads to use for travel time. If set to
0,cpu_count*2will be used. velocity_model-
Velocity model for the ray tracer.
implementation:pyrocko | scikit-fmm-
Implementation of the Fast Marching Method. Pyrocko only supports first-order FMM for now.
Visualizing 3D Models
For quality check, all 3D velocity models are exported to vtk/ folder as .vti files. Use ParaView to inspect and explore the velocity models.
 Seismic velocity model of the Utah FORGE testbed site, visualized in ParaView.
Seismic velocity model of the Utah FORGE testbed site, visualized in ParaView.